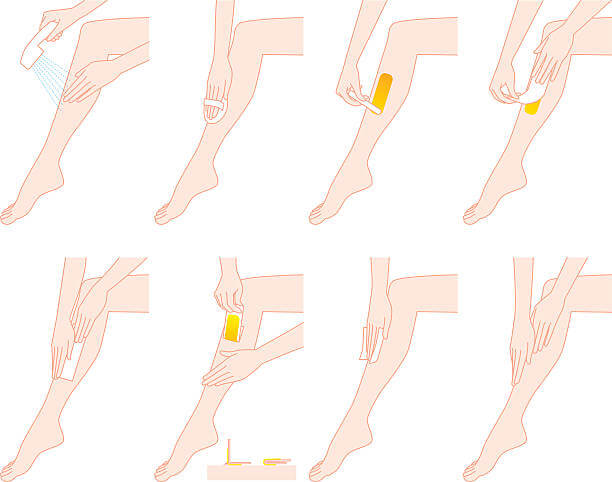
Treating Psoriasis: A Professional's Guide
The Professionals Guide to Treating Psoriasis
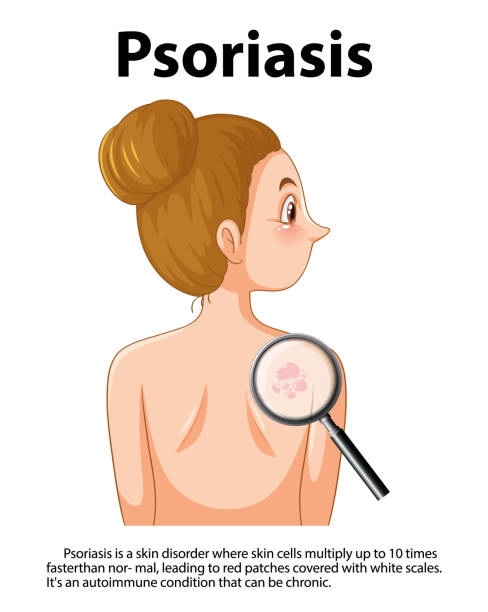
Psoriasis is a chronic, autoimmune skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by red, scaly patches that can appear on various parts of the body, including the scalp, elbows, knees, and torso. While there is no cure for psoriasis, there are several effective treatment options available that can help manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for those living with the condition.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various treatment options for psoriasis, including topical therapies, phototherapy, systemic medications, and biologic drugs. We will also discuss the importance of a multidisciplinary approach to managing psoriasis and the role of lifestyle modifications in promoting overall health and well-being.
Understanding Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a complex condition that involves an overactive immune system. In people with psoriasis, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, causing them to multiply rapidly and form thick, scaly patches. While the exact cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, it is believed to be influenced by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
There are several different types of psoriasis, including plaque psoriasis, guttate psoriasis, inverse psoriasis, pustular psoriasis, and erythrodermic psoriasis. Each type has its own unique characteristics and may require different treatment approaches.
Topical Therapies
Topical therapies are the first-line treatment for mild to moderate psoriasis. These medications are applied directly to the affected areas of the skin and can help reduce inflammation, slow skin cell growth, and remove scales.
Some common topical therapies for psoriasis include:
- Corticosteroids: These medications help reduce inflammation and itching.
- Vitamin D analogues: These medications help slow skin cell growth and reduce inflammation.
- Retinoids: These medications help reduce scaling and inflammation.
- Calcineurin inhibitors: These medications help reduce inflammation and itching.
Topical therapies are generally well-tolerated, but they may cause side effects such as skin irritation, thinning of the skin, or increased sun sensitivity.
Phototherapy
Phototherapy, also known as light therapy, is a treatment option for moderate to severe psoriasis. It involves exposing the affected areas of the skin to controlled amounts of natural or artificial ultraviolet (UV) light.
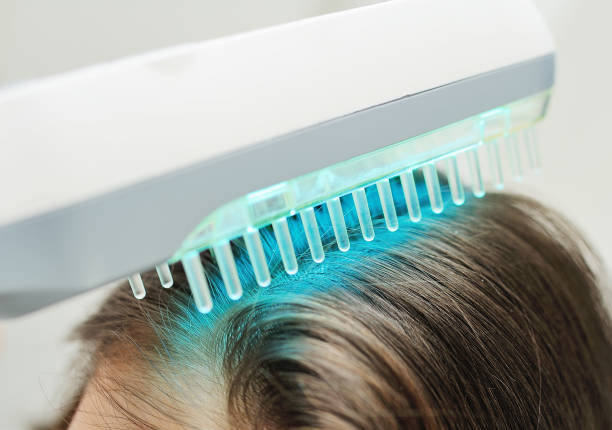

There are several different types of phototherapy, including:
- Narrowband UVB: This type of phototherapy uses a specific wavelength of UVB light to slow skin cell growth and reduce inflammation.
- Broadband UVB: This type of phototherapy uses a wider range of UVB wavelengths to treat psoriasis.
- PUVA: This type of phototherapy combines the use of a medication called psoralen with exposure to UVA light.
Phototherapy is generally well-tolerated, but it may cause side effects such as skin redness, itching, or increased sun sensitivity.
Systemic Medications
Systemic medications are oral or injectable medications that are used to treat moderate to severe psoriasis. These medications work by targeting the underlying causes of psoriasis and can help reduce inflammation and slow skin cell growth.
Some common systemic medications for psoriasis include:
- Methotrexate: This medication helps reduce inflammation and slow skin cell growth.
- Cyclosporine: This medication helps suppress the overactive immune system and reduce inflammation.
- Acitretin: This medication helps slow skin cell growth and reduce scaling.
Systemic medications can be effective in treating psoriasis, but they may also cause side effects such as nausea, fatigue, or liver or kidney problems.
Biologic Drugs
Biologic drugs are a newer class of medications that are used to treat moderate to severe psoriasis. These medications are made from living organisms and work by targeting specific parts of the immune system to reduce inflammation and slow skin cell growth.
Some common biologic drugs for psoriasis include:
- TNF-alpha inhibitors: These medications help reduce inflammation by blocking a specific protein called tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha).
- IL-17 inhibitors: These medications help reduce inflammation by blocking a specific protein called interleukin-17 (IL-17).
- IL-23 inhibitors: These medications help reduce inflammation by blocking a specific protein called interleukin-23 (IL-23).
Biologic drugs can be highly effective in treating psoriasis, but they may also cause side effects such as infections, allergic reactions, or an increased risk of certain types of cancer.
A Multidisciplinary Approach
Managing psoriasis often requires a multidisciplinary approach that involves a team of healthcare professionals, including dermatologists, rheumatologists, primary care physicians, and mental health professionals.
A multidisciplinary approach can help ensure that all aspects of the patient's health are addressed, including physical, emotional, and social well-being. This may involve a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle modifications, and psychological support.
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle modifications can also play an important role in managing psoriasis. Some key lifestyle factors that can impact psoriasis include stress, diet, and physical activity.
Stress can trigger or worsen psoriasis flare-ups, so it's important to find healthy ways to manage stress, such as through relaxation techniques, exercise, or counseling. A healthy diet that is rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, may also help reduce inflammation and improve overall health. Regular physical activity can also help reduce stress, improve mood, and promote overall well-being.
Conclusion
Psoriasis is a complex and chronic skin condition that can have a significant impact on a person's physical and emotional well-being. However, with the right treatment approach and lifestyle modifications, it is possible to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
By working closely with a team of healthcare professionals and making lifestyle changes to support overall health and well-being, individuals with psoriasis can take an active role in managing their condition and living their best lives. With continued research and advancements in treatment options, there is hope for a future where psoriasis is more effectively managed and individuals with the condition can thrive.
CONTINUE READING
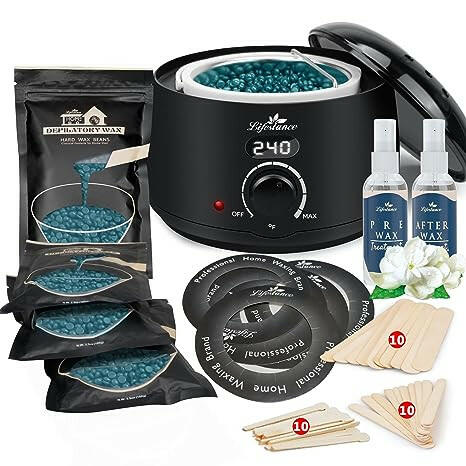
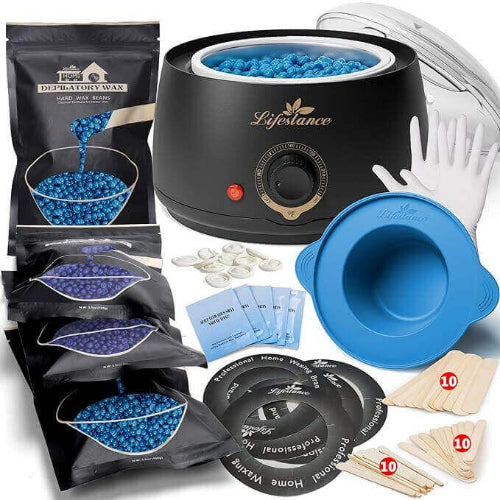
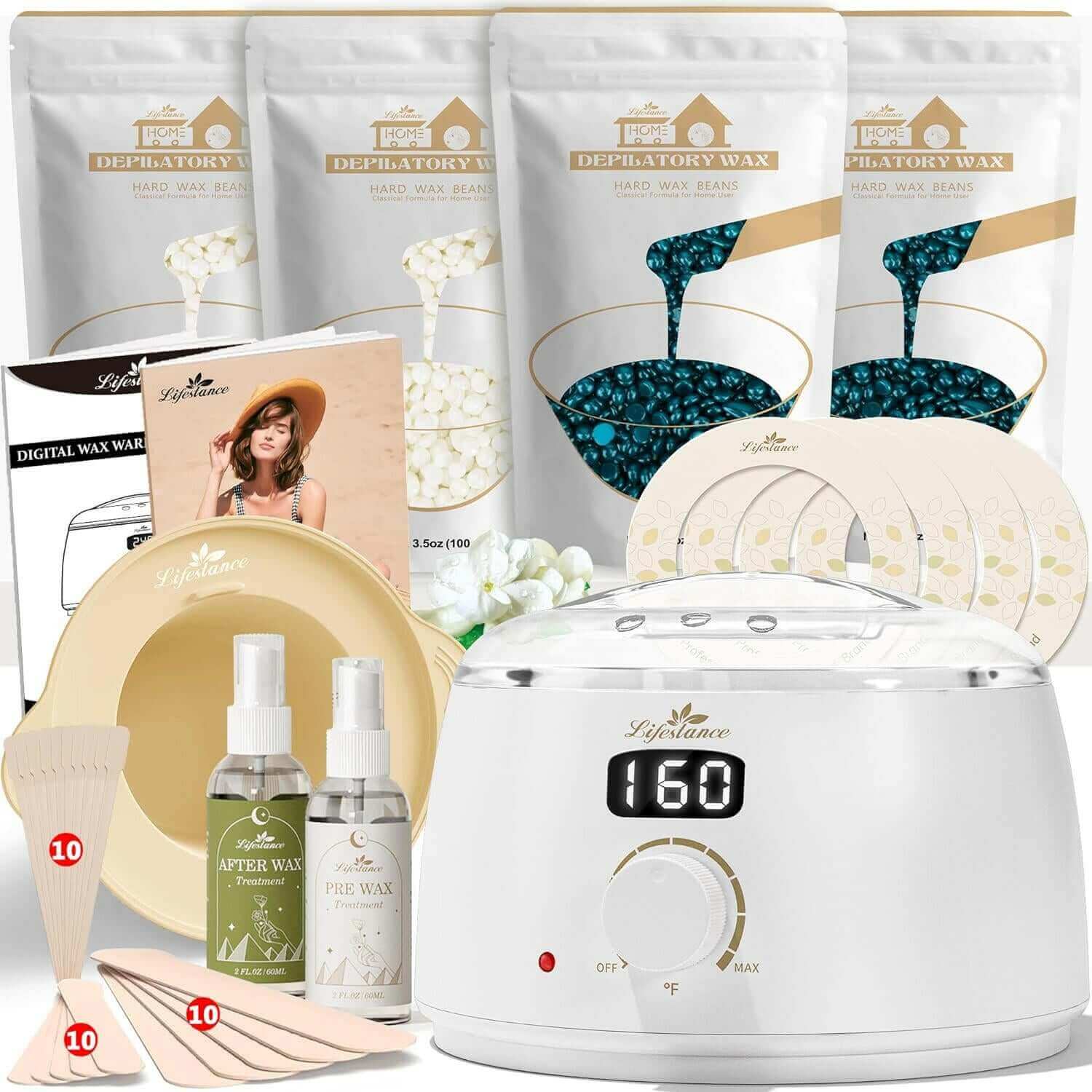
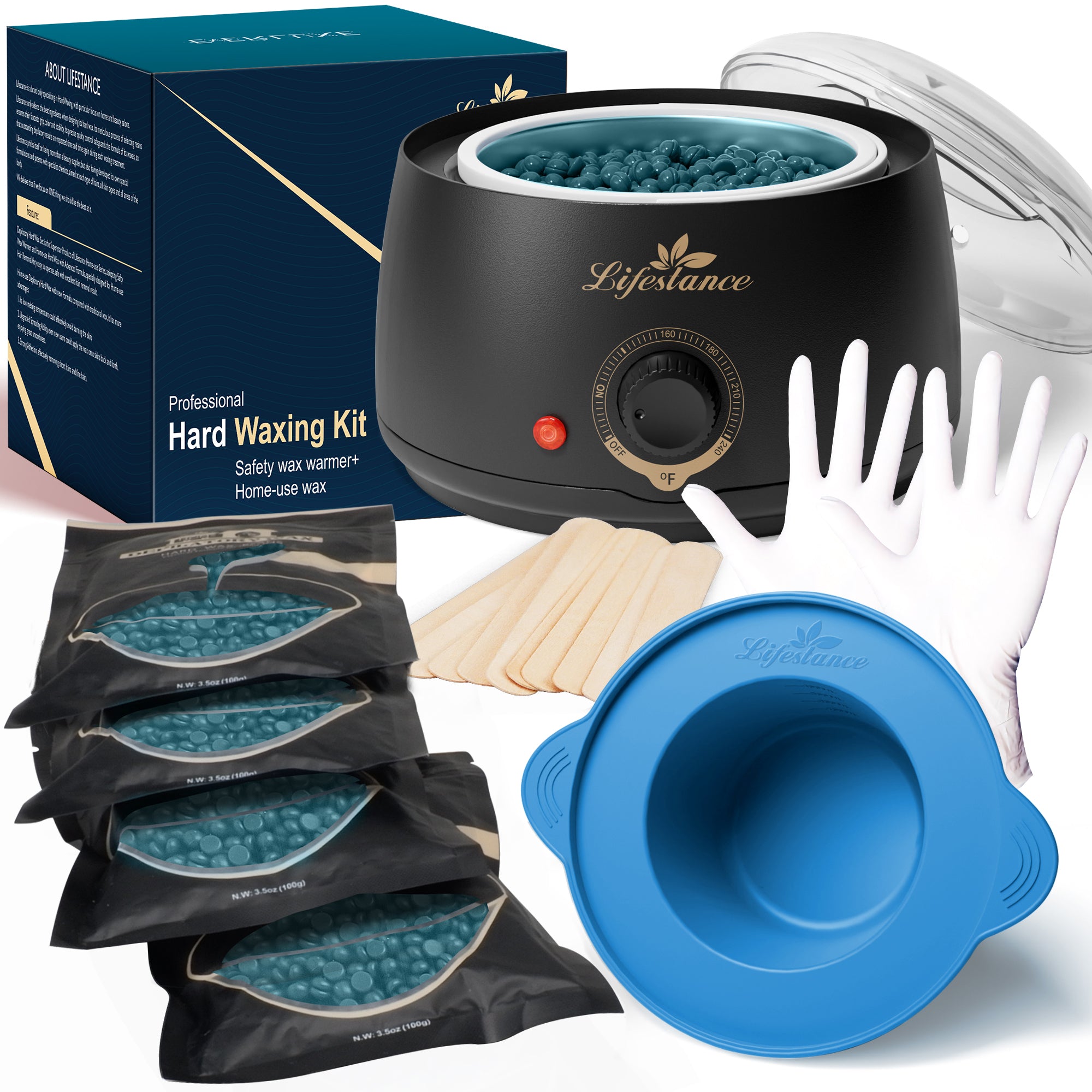
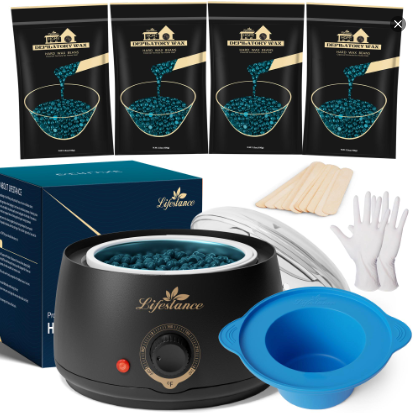
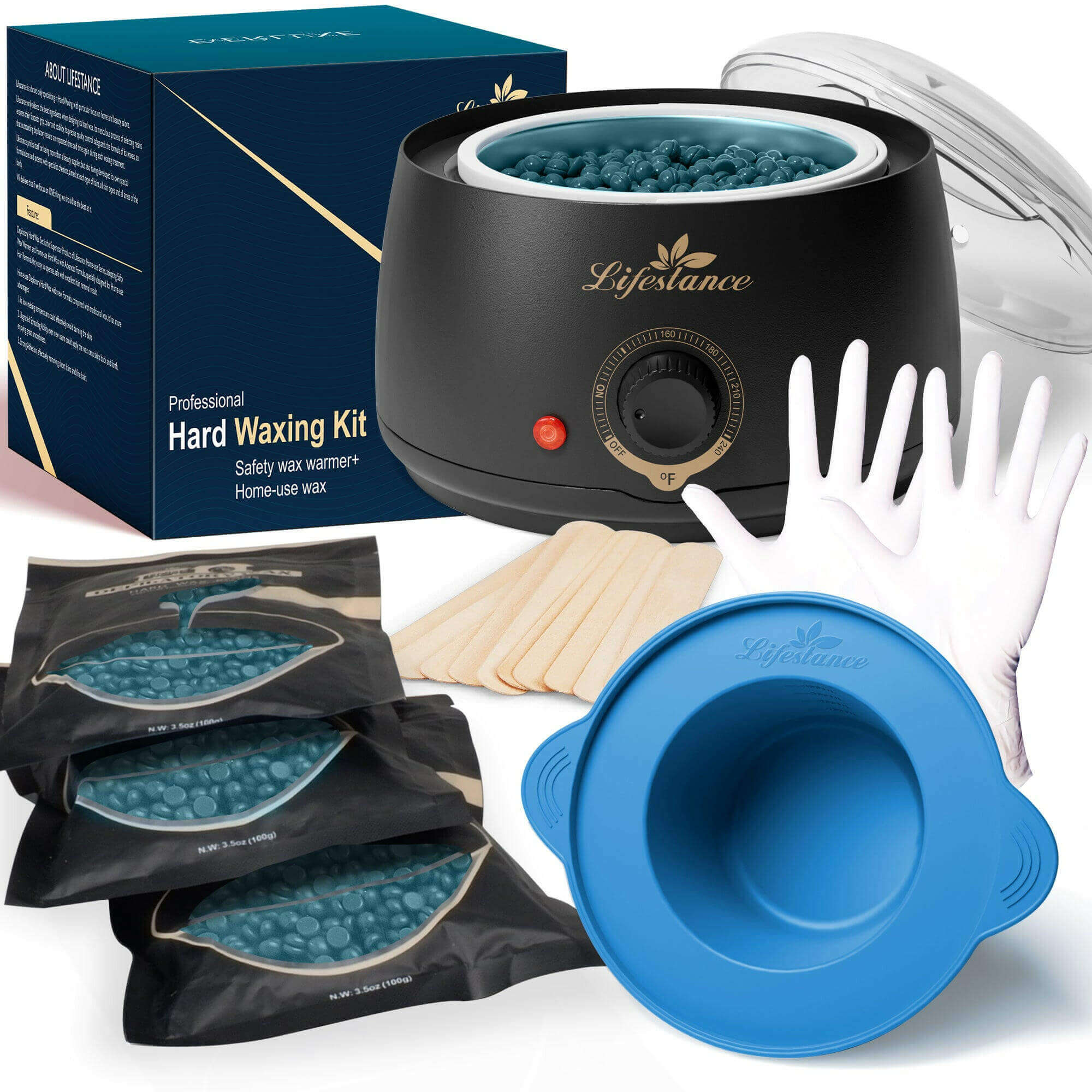
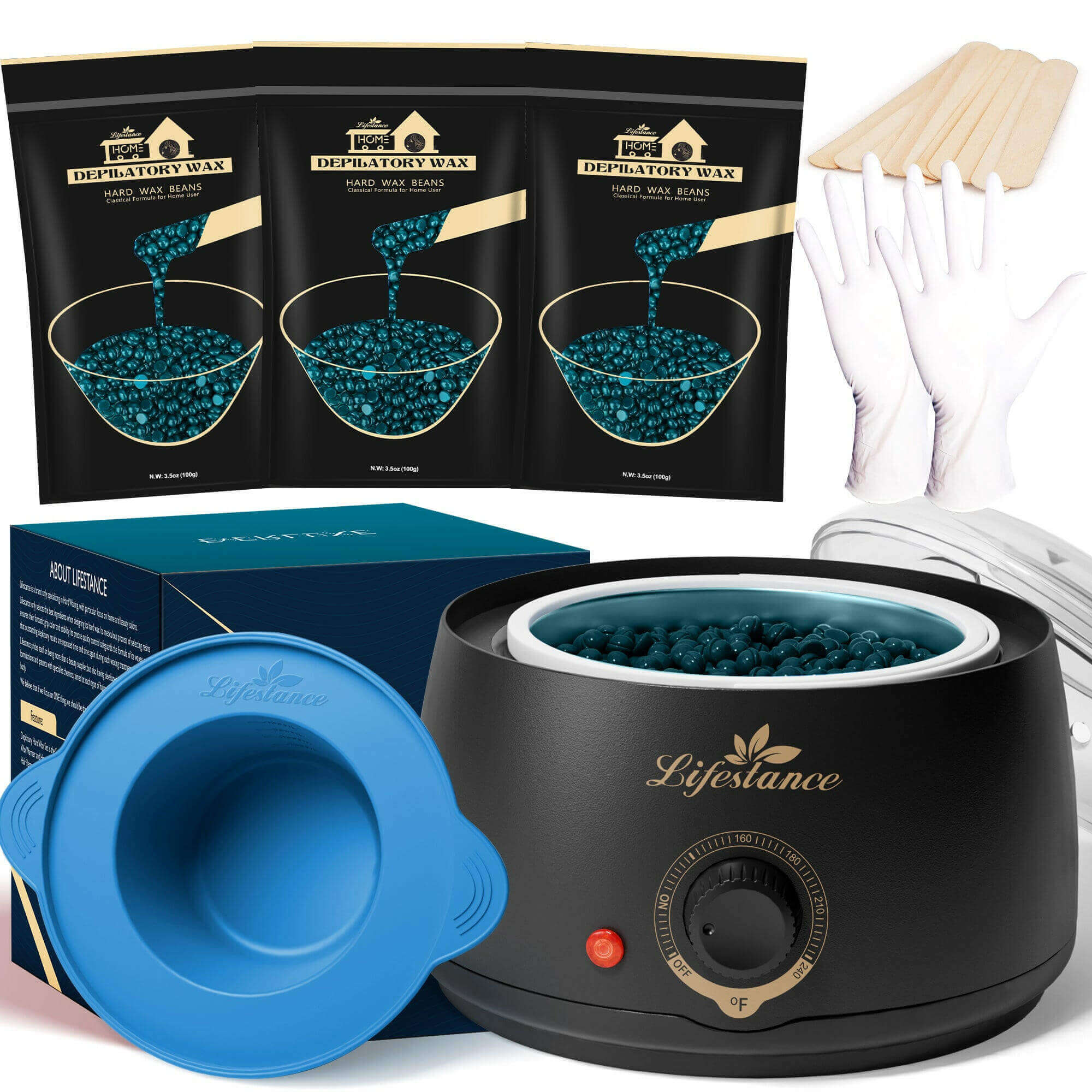
Waxing Product
Why Choose Us
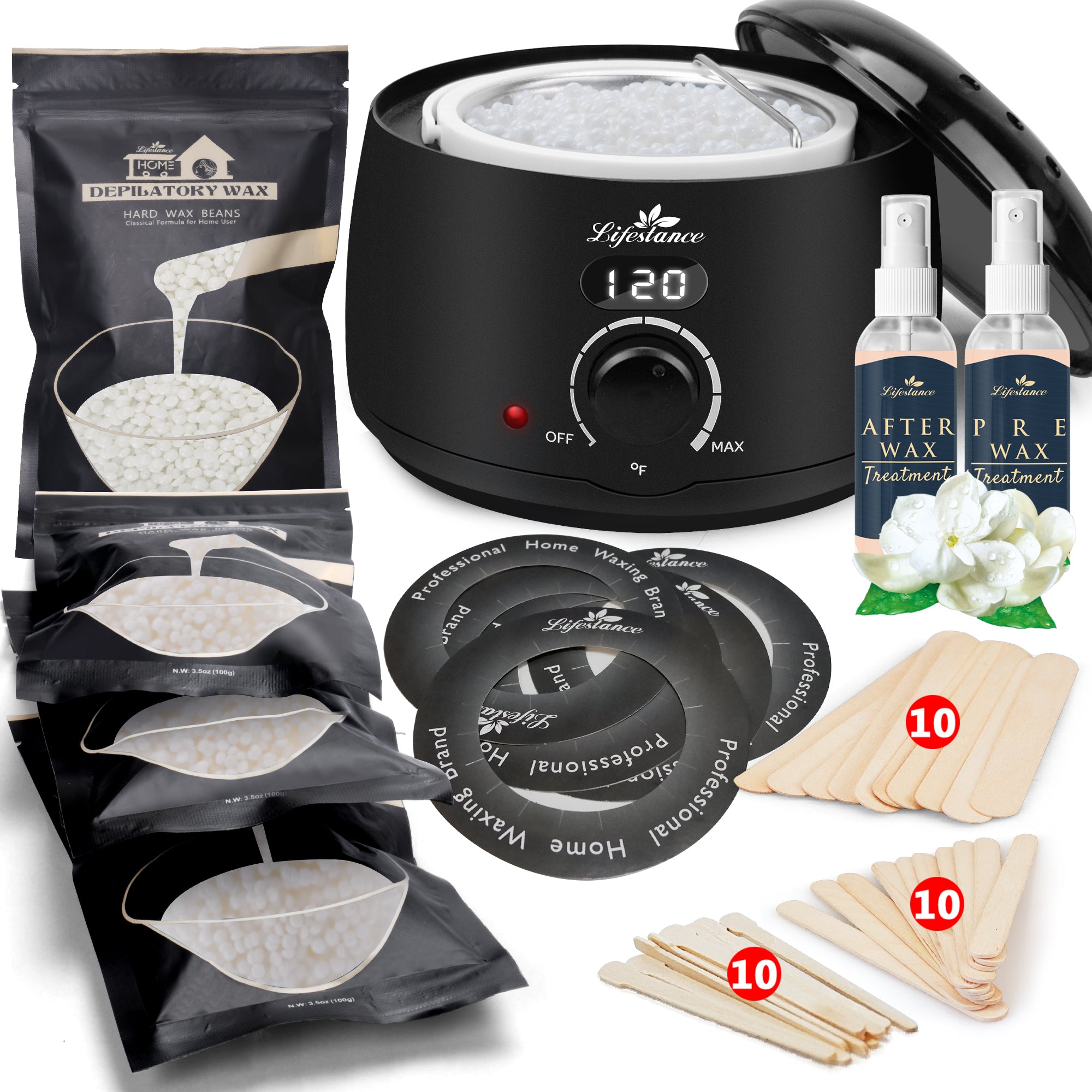
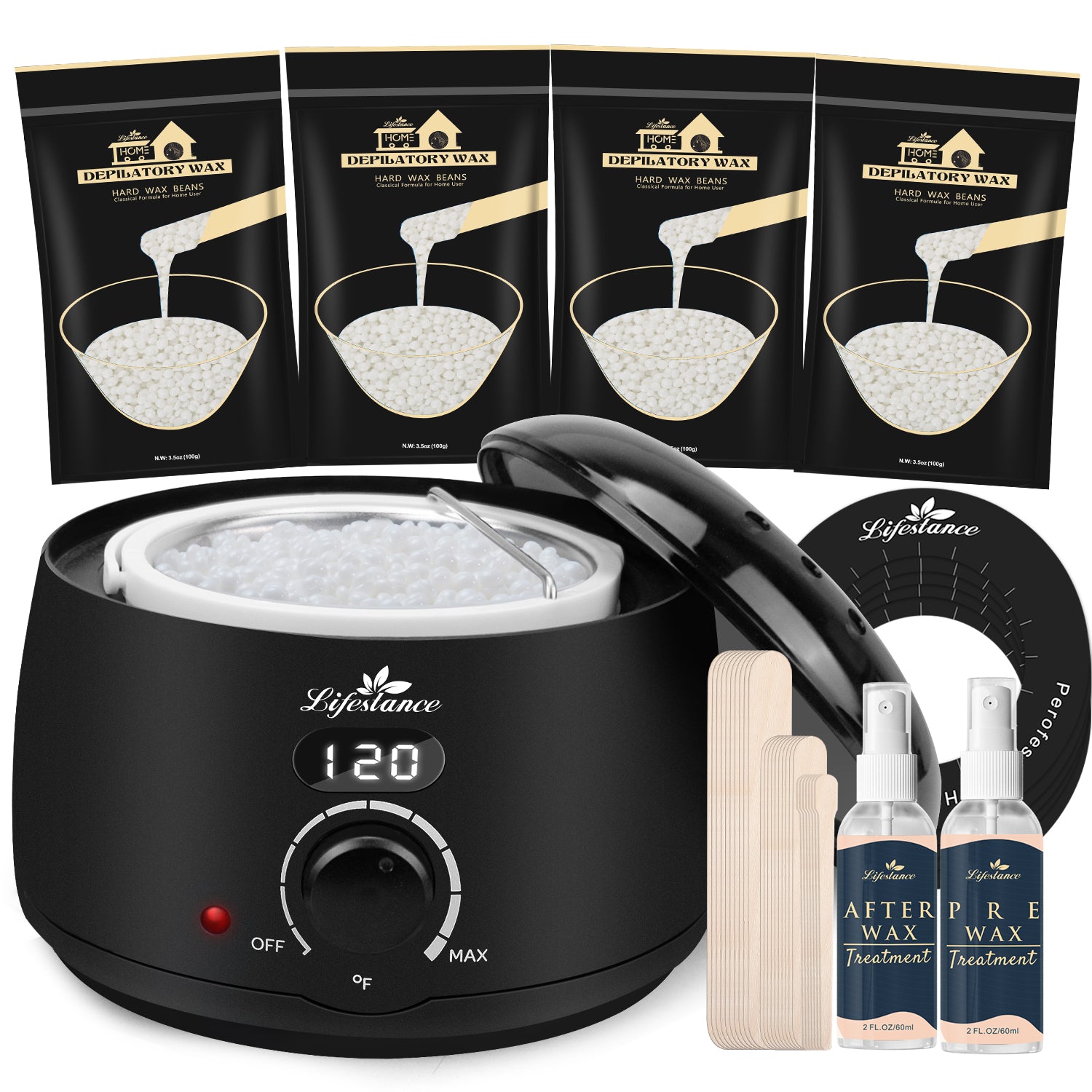
At Lifestance, we understand that everyone's hair removal needs are unique. That's why we offer a wide range of professional waxing kits to ensure that different skin types, body hair types and budgets are catered for. Whether you are a seasoned beauty professional or a first-time self-service waxer, we are committed to providing you with an exceptional product and service experience.
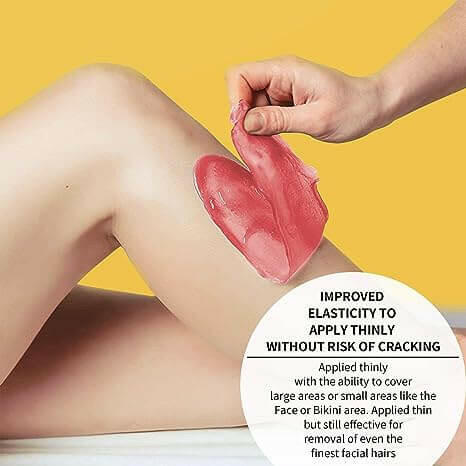
Safety and ComfortOur waxing products are made with natural and gentle formulas that have passed rigorous testing and certification to ensure that skin irritation is minimized. At the same time, our patented heating technology allows for precise temperature control, so you can enjoy a comfortable waxing experience.
Professional Quality Convenient and PracticalWhether you're a licensed esthetician or a homeowner, Lifestance has you covered. Our kits contain everything you need and are so easy to use that even beginners can master them. The quality of our products is outstanding, ensuring smooth, flawless skin.
Innovative ideas and serviceWe are constantly developing innovative technologies and formulas to provide our customers with an unprecedented hair removal experience. Whatever your questions or needs, our team of professionals is always on hand to provide you with personalized service and guidance.
When you choose Lifestance, you choose beauty, comfort, convenience and professionalism. We are dedicated to providing you with an exceptional hair removal experience that will help you look and feel your best.